Servitisation
Unlocking Value Through Servitisation
Discover how businesses are transforming from product-based models to service-driven strategies. This servitisation journey empowers long-term growth, customer loyalty, and competitive advantage in today's evolving marketplace.
Strategy Fails Without People Who Can Deliver It
Many companies have the right vision. The challenge is finding the people who can make it real. New
models require new roles, new leadership, and new capabilities—from digital service architects and
predictive engineers to outcome-based commercial managers. But most org charts weren't built for this.
And many HR strategies haven't caught up.
70% of transformation failures are linked to people and capability issues—not
technology. We're here to close that gap.
Explore How Your Workforce Needs Evolve at Each Stage
As businesses move from product-centric models to fully servitised, autonomous service delivery,
workforce needs evolve dramatically. Each stage of transformation comes with distinct
expectations around talent, leadership, and structure — and organisations that adapt their
people strategy accordingly are far more likely to succeed. Here's how talent requirements shift across
the five stages:
The Servitisation Role Accountability Framework
Clarity. Alignment. Execution.The Servitisation Role Accountability Framework is our proprietary framework for aligning people, roles, and results in service-led organisations. It brings structure to transformation by defining 4 core accountability domains and 20 targeted sub-accountabilities that reflect the real-world responsibilities needed to deliver service excellence.
This matrix helps organisations:
- Clarify who is accountable for what across evolving service functions
- Align job roles, team structures, and capability expectations with your business model
- Drive focused execution at every level, from frontline teams to executive leadership
- Align job roles, team structures, and capability expectations with your business model
It's a practical, people-focused tool designed for HR leaders, operational managers, and transformation teams who need to translate servitisation goals into workforce action.
The Servitisation Accountability Framework connects strategy to structure — so the right people are focused on the right outcomes at every stage of your transformation.
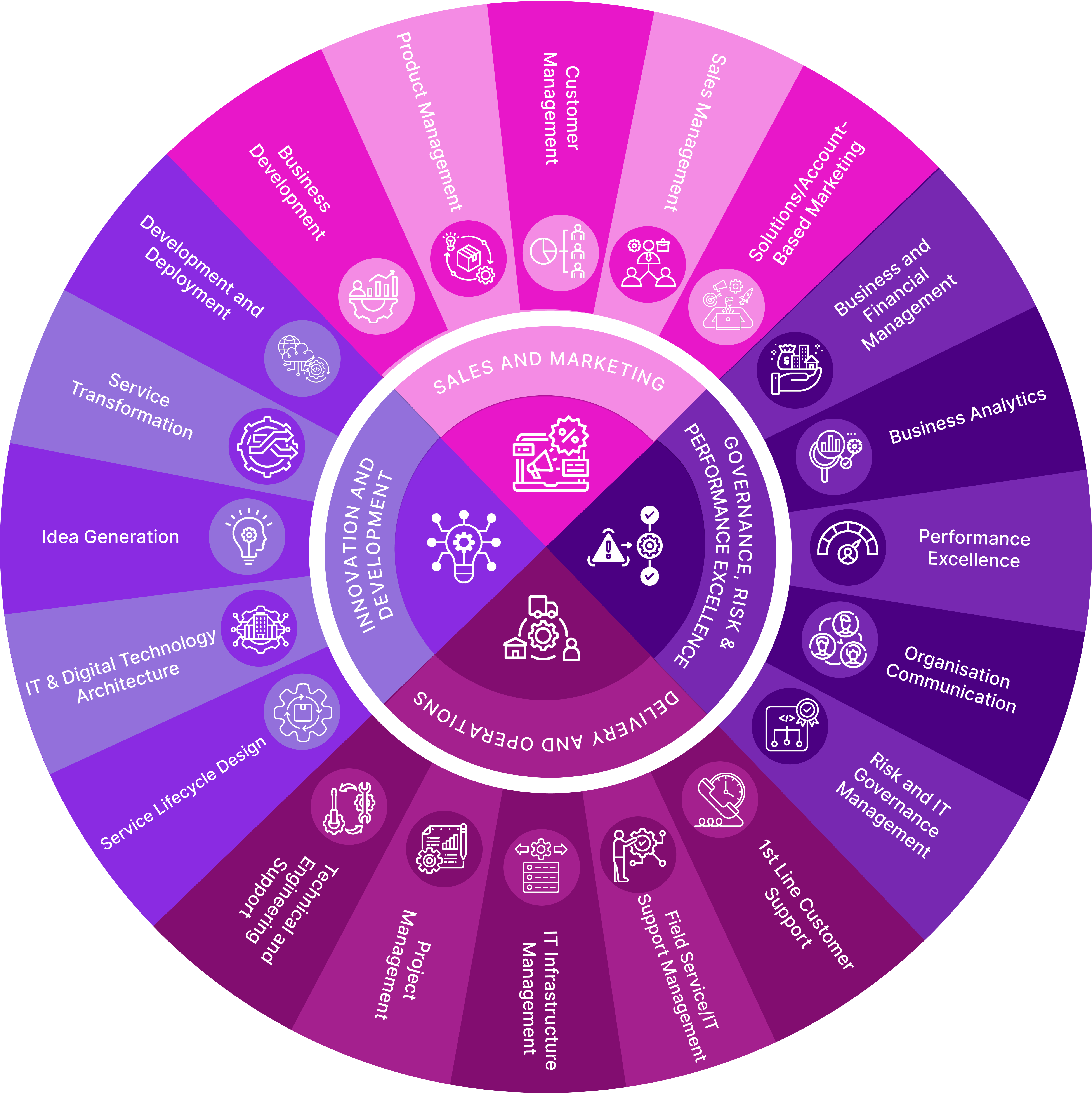
A visual model aligning 4 domains and 20 sub-accountabilities that shape how service-led organisations think, operate, and transform
Depending on the Business Context, Servitisation Stage and Specific Job Role the general overview by career level is as below:
EXECUTIVE & SENIOR LEADERSHIP
Focus:Strategic planning, partnerships, transformation leadership, market expansion, organisational risk and performance.
DIRECTORS & SENIOR MANAGERS
Focus:Translating strategy into programs, leading large functions, overseeing portfolios or divisions, stakeholder engagement.
TEAM LEADERS & SUPERVISORS
Focus:Operational execution, team coordination, short-term improvement initiatives, process alignment, escalation handling.
SPECIALISTS & SENIOR TECHNICAL ROLES
Focus:Subject matter expertise, driving technical projects, supporting new service innovation, quality and compliance.
TECHNICAL PROFESSIONALS & MID LEVEL ROLES
Focus:Day-to-day service delivery, engineering support, reporting, some participation in pilot programs and improvement tasks.
ENTRY-LEVEL & ASSOCIATE ROLES
Focus:Execution-level tasks, frontline support, learning by doing, supporting documentation, process adherence.
Depending on the Business Context, Servitisation Stage and Specific Job Role the percentage of time spent in the 4 core accountability domains and 20 targeted sub-accountabilities of the Servitisation Accountability Framework will vary, see below a general overview of stage-by-stage evolution of Focus and Time Bias.

 STAGE 1
STAGE 2
STAGE 3
STAGE 4
STAGE 5
STAGE 1
STAGE 2
STAGE 3
STAGE 4
STAGE 5
Product-Based (Transactional Sales)
Focus:
Cost control, asset uptime, reactive support
Time Bias:
- Heavy in Delivery & Operations for most levels
- Low on Innovation, even for senior roles
- Executives focus on Sales & Ops efficiency
Product + Service (Basic Support Contracts)
Focus:
Bundled services, service SLAs, customer satisfaction
Time Bias:
- 1st Line Support and Field Services become more central
- Product Management and Customer Management time rises
- Supervisors start engaging more with Performance Excellence
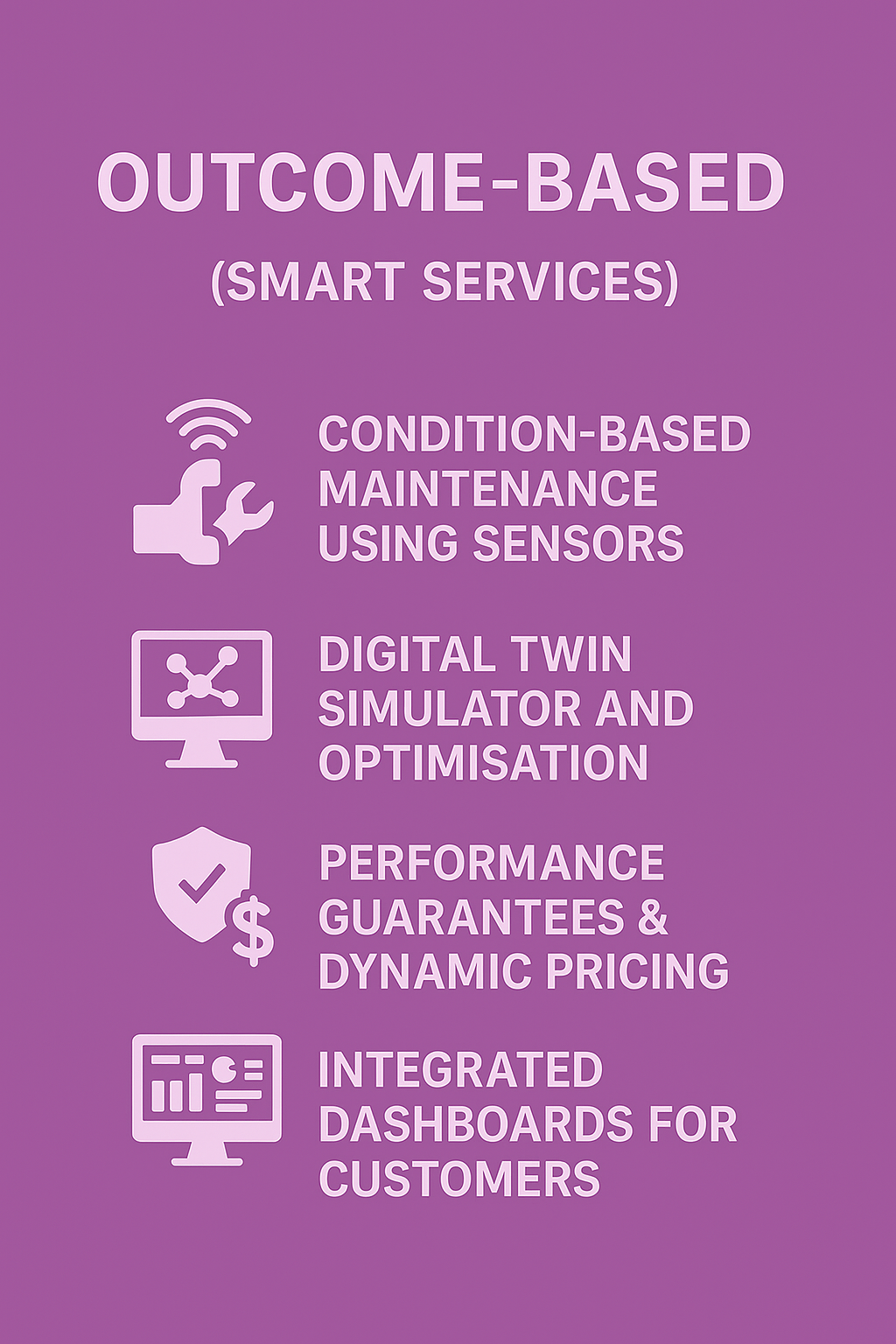
Outcome-Based Services (Service Agreements)
Focus:
Performance-based contracts, uptime guarantees
Time Bias:
- Rise in Governance & Risk time across levels
- Mid- to senior-levels increasingly involved in Service Lifecycle Design and IT Architecture
- Analytics and Project Management gain importance
Advanced Solutions (Digital + Consulting Integration)
Focus:
Co-creation, integration of digital & consulting
Time Bias:
- Significant increase in Innovation & Development time, especially for leadership and technical specialists
- Solutions/Account-Based Marketing and Business Development dominate senior sales focus
- Field support shifts to remote diagnostics + predictive analytics
Servitised Ecosystem (Platform + Partnership-Oriented)
Focus:
Ecosystem orchestration, platform-led revenue, co-innovation
Time Bias:
- Executive and Director time is heavily weighted toward Governance, Innovation, and Strategic Sales
- Strong growth in time for IT Architecture, Service Transformation, and Idea Generation roles
- Entry/Mid levels may see more cross-functional and data-focused work